GRAVITY GOODS ROPEWAY
2.2 Detailed Topographical Survey
The detailed topographical survey of a gravity
ropeway site serves the following two important
functions:
It provides the detailed map of the ropeway
site and surrounding areas, giving all the
details of those features which are important
while designing gravity ropeway. Existence of
adjoining structures, obstructions and terrain
characteristics are obtained from the site
tachometric survey.
The site tachometric survey provides definite,
secured and well documented axis pegs.
These pegs will be used while laying out
the foundation blocks of the gravity ropeway
during construction.
If the ropeway alignment is perpendicular to the
contour, then the survey of profile along the centre
line will be sufficient. But in case of transverse
slope, the surveyor needs to record the cross
sections at certain intervals of the cross sections
or slope.
2.2.1 Tachometric survey:
Tachometric survey calculates the elevations at
different points along the alignment of ropeway
to get the ground profile for the centre line of
Figure 7
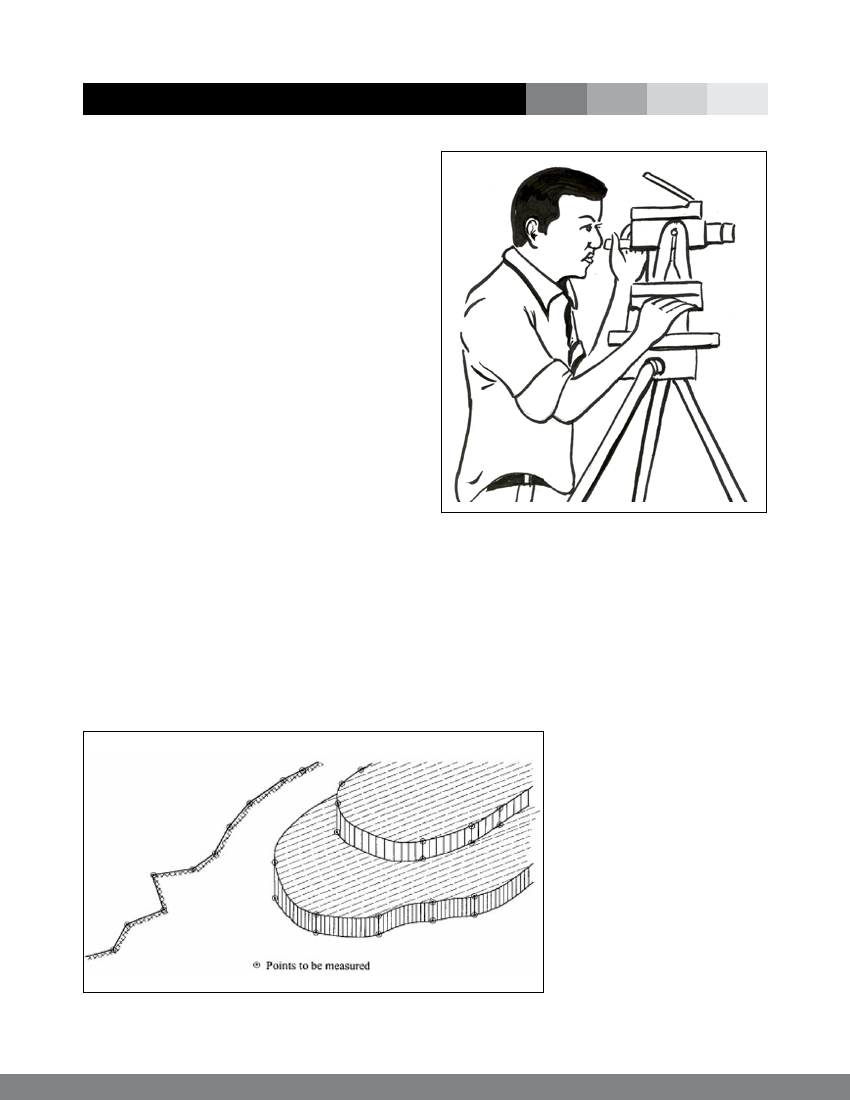
Figure 8: Schematic diagram of Theodolite
the ropeway alignment. The survey points (staff
points) should be taken at different intervals
of slopes, terraces, fields and other features
representing the actual topography of the ground
as shown in the sketch below in figure 7.
The procedure for survey is as follows:
Once the ropeway
alignment is finalised,
fix the centre line of the
gravity ropeway securing two
permanent pegs A and B at
the estimated position of the
sheave at each station. The
pegs should be firmly fixed
into the ground so that it
remains intact throughout
the construction period. For
each peg A and B, choose at
least three point of references
each in 10 metres intervals.
Measure the horizontal
distances from the points of
10